The Radio Transmitter
Transmitter Block Diagrams
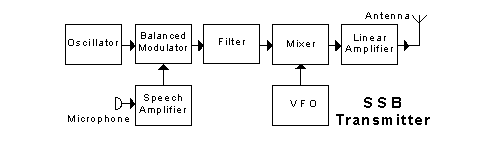
In the transmitter block diagram shown, the "oscillator"
-
is variable in frequency
-
generates an audio frequency tone during tests
-
Correct Answeruses a crystal for good frequency stability
-
may have a calibrated dial
Tags: none

In the transmitter block diagram shown, the "balanced modulator"
-
balances the high and low frequencies in the audio signal
-
Correct Answerperforms double sideband suppressed carrier modulation
-
acts as a tone control
-
balances the standing wave ratio
Correct answer: performs double sideband suppressed carrier modulation
In an SSB transmitter, the balanced modulator combines the audio signal with the carrier in such a way that the carrier is cancelled out.
This produces a double sideband suppressed carrier (DSB-SC) signal, which contains:
- an upper sideband
- a lower sideband
- no carrier component
This signal is then passed to a filter to remove one sideband, producing the final SSB signal.
- It does not adjust audio frequency balance.
- It is not a tone control.
- It is unrelated to standing wave ratio.
Therefore, the balanced modulator performs double sideband suppressed carrier modulation.
Last edited by jim.carroll. Register to edit
Tags: none

In the transmitter block diagram shown, the "filter"
-
removes mains hum from the audio signal
-
suppresses unwanted harmonics of the RF signal
-
Correct Answerremoves one sideband from the modulated signal
-
removes the carrier component from the modulated signal
Correct answer: removes one sideband from the modulated signal
In an SSB transmitter, the balanced modulator produces a double sideband suppressed carrier (DSB-SC) signal. This signal contains both the upper and lower sidebands, but only one sideband is desired for transmission.
The filter following the balanced modulator is a narrow bandpass filter that selects the wanted sideband and rejects the unwanted sideband. This process creates a true single sideband (SSB) signal.
- removes mains hum from the audio signal is the function of audio filtering in the microphone or speech amplifier stages, not the RF filter shown here.
- suppresses unwanted harmonics of the RF signal is typically done by output filtering after the power amplifier, not at this stage of modulation.
- removes the carrier component from the modulated signal is performed by the balanced modulator itself, not by the filter.
Therefore, the filter’s purpose in this block diagram is to remove one sideband from the modulated signal.
Last edited by jim.carroll. Register to edit
Tags: none

In the transmitter block diagram shown, the "mixer"
-
adds the correct proportion of carrier to the SSB signal
-
mixes the audio and RF signals in the correct proportions
-
Correct Answertranslates the SSB signal to the required frequency
-
mixes the two sidebands in the correct proportions
Correct answer: translates the SSB signal to the required frequency
In this SSB transmitter, the balanced modulator and filter first generate a clean single sideband signal at an intermediate frequency. The mixer then combines this SSB signal with the signal from the VFO.
Mixing produces sum and difference frequencies, effectively shifting the SSB signal to the desired transmit frequency band. This process is called frequency translation or upconversion.
- adds the correct proportion of carrier to the SSB signal is incorrect, the carrier remains suppressed in an SSB transmitter unless deliberately reinserted elsewhere.
- mixes the audio and RF signals in the correct proportions describes the function of the balanced modulator earlier in the chain, not the mixer.
- mixes the two sidebands in the correct proportions is incorrect because only one sideband exists after the filter stage.
Therefore, the mixer’s role is to translate the SSB signal to the required frequency.
Last edited by jim.carroll. Register to edit
Tags: none

In the transmitter block diagram shown, the "linear amplifier"
-
has all components arranged in-line
-
Correct Answeramplifies the modulated signal with no distortion
-
aligns the two sidebands correctly
-
removes any unwanted amplitude modulation from the signal
Tags: none

In the transmitter block diagram shown, the "VFO" is
-
a voice frequency oscillator
-
a varactor fixed oscillator
-
a virtual faze oscillator
-
Correct Answera variable frequency oscillator
Tags: none

In the transmitter block diagram shown, the "master oscillator" produces
-
Correct Answera steady signal at the required carrier frequency
-
a pulsating signal at the required carrier frequency
-
a 800 Hz signal to modulate the carrier
-
a modulated CW signal
Tags: none

In the transmitter block diagram shown, the "driver buffer"
-
filters any sharp edges from the input signal
-
drives the power amplifier into saturation
-
Correct Answerprovides isolation between the oscillator and power amplifier
-
changes the frequency of the master oscillator signal
Correct answer: provides isolation between the oscillator and power amplifier
In a CW transmitter, the master oscillator must maintain a stable frequency. Any changes in load can cause frequency pulling or drift.
The driver buffer is placed between the oscillator and the power amplifier to prevent this. It presents a constant, stable load to the oscillator while supplying sufficient drive to the next stage. This isolation ensures that variations in the power amplifier or antenna do not affect the oscillator frequency.
- Filtering sharp edges is the role of filters or waveform-shaping circuits, not a buffer amplifier.
- Driving the power amplifier into saturation is undesirable in this context and is not the buffer’s function.
- Changing frequency requires mixers, modulators, or multipliers, not a buffer stage.
Therefore, the driver buffer’s purpose is to provide isolation between the oscillator and the power amplifier.
Last edited by jim.carroll. Register to edit
Tags: none

In the transmitter block diagram shown, the "Morse key"
-
turns the DC power to the transmitter on and off
-
Correct Answerallows the oscillator signal to pass only when the key is depressed
-
changes the frequency of the transmitted signal when the key is depressed
-
adds an 800 Hz audio tone to the signal when the key is depressed
Correct answer: allows the oscillator signal to pass only when the key is depressed
In a CW (continuous wave) transmitter, the Morse key is used to control when the RF carrier is transmitted.
When the key is:
- depressed → the RF signal from the oscillator is allowed to pass through to the amplifier stages and antenna
- released → the RF signal is interrupted
This produces the on–off keying required for Morse code transmission.
- It does not switch the entire DC power to the transmitter.
- It does not change the transmitted frequency.
- CW transmission does not involve adding an audio tone to the RF signal.
Therefore, the Morse key allows the oscillator signal to pass only when the key is depressed.
Last edited by jim.carroll. Register to edit
Tags: none

In the transmitter block diagram shown, the "power amplifier"
-
Correct Answerneed not have linear characteristics
-
amplifies the bandwidth of its input signal
-
must be adjusted during key-up conditions
-
should be water-cooled
Correct answer: need not have linear characteristics
In a CW (continuous wave) transmitter, the signal is a single RF carrier that is simply switched on and off by the Morse key. There is no amplitude or phase modulation that must be preserved.
Because the waveform contains no modulation information, the power amplifier does not need to operate linearly. It can be run in a more efficient non-linear class (such as Class C) without distorting the transmitted signal.
- amplifies the bandwidth of its input signal is incorrect, amplifiers increase power or voltage, not bandwidth.
- must be adjusted during key-up conditions is incorrect, tuning and adjustment are normally done with the transmitter keyed and producing RF.
- should be water-cooled depends on power level and design, not on the basic function of a CW power amplifier.
Therefore, in a CW transmitter the power amplifier need not have linear characteristics.
Last edited by jim.carroll. Register to edit
Tags: none
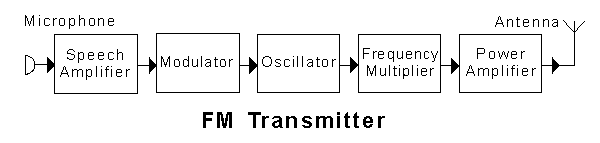
In the transmitter block diagram shown, the "speech amplifier"
-
Correct Answeramplifies the audio signal from the microphone
-
is a spectral equalization entropy changer
-
amplifies only speech, while discriminating against background noises
-
shifts the frequency spectrum of the audio signal into the RF region
Tags: none

In the transmitter block diagram shown, the "modulator"
-
is an amplitude modulator with feedback
-
is an SSB modulator with feedback
-
causes the speech waveform to gate the oscillator on and off
-
Correct Answercauses the speech waveform to shift the frequency of the oscillator
Correct answer: causes the speech waveform to shift the frequency of the oscillator
In an FM transmitter, the modulator applies the audio (speech) signal to the oscillator in such a way that the oscillator’s frequency varies in accordance with the speech waveform.
This produces frequency modulation:
-
the carrier frequency shifts above and below its centre frequency
-
the amount of shift depends on the amplitude of the speech signal
-
It is not an amplitude modulator.
-
SSB modulation is a different process.
-
Gating the oscillator on and off would produce CW, not FM.
Therefore, the modulator causes the speech waveform to shift the frequency of the oscillator.
Last edited by jim.carroll. Register to edit
Tags: none

In the transmitter block diagram shown, the "oscillator" is
-
an audio frequency oscillator
-
Correct Answera variable frequency RF oscillator
-
a beat frequency oscillator
-
a variable frequency audio oscillator
Correct answer: a variable frequency RF oscillator
In an FM transmitter, the oscillator generates the radio frequency (RF) carrier signal that is to be modulated by the audio input.
This RF signal is then passed through stages such as the frequency multiplier and power amplifier before being transmitted.
- An audio frequency oscillator would produce audio signals, not RF.
- A beat frequency oscillator (BFO) is used in receivers for CW detection.
- A variable frequency audio oscillator would not generate an RF carrier.
Therefore, the oscillator in the transmitter is a variable frequency RF oscillator.
Last edited by jim.carroll. Register to edit
Tags: none

In the transmitter block diagram shown, the "frequency multiplier"
-
translates the frequency of the modulated signal into the RF spectrum
-
changes the frequency of the speech signal
-
Correct Answerproduces a harmonic of the oscillator signal
-
multiplies the oscillator signal by the speech signal
The Frequency Multiplier stage is an RF amplifier with a tuned output - the output tuned to a harmonic of the input signal.
Last edited by cmscouler. Register to edit
Tags: none

In the transmitter block diagram shown, the "power amplifier"
-
increases the voltage of the mains to drive the antenna
-
amplifies the audio frequency component of the signal
-
amplifies the selected sideband to a suitable level
-
Correct Answeramplifies the RF signal to a suitable level
Tags: none
The signal from an amplitude modulated transmitter consists of
-
Correct Answera carrier and two sidebands
-
a carrier and one sideband
-
no carrier and two sidebands
-
no carrier and one sideband
Correct answer: a carrier and two sidebands
In amplitude modulation (AM), the transmitted signal consists of:
- a central carrier frequency
- an upper sideband
- a lower sideband
The sidebands are produced by the modulation process and contain the information from the audio signal.
- A carrier and one sideband describes single sideband (SSB).
- No carrier and two sidebands describes double sideband suppressed carrier (DSB-SC).
- No carrier and one sideband describes suppressed-carrier SSB.
Therefore, an AM signal consists of a carrier and two sidebands.
Last edited by jim.carroll. Register to edit
Tags: none
The signal from a frequency modulated transmitter has
-
an amplitude which varies with the modulating waveform
-
Correct Answera frequency which varies with the modulating waveform
-
a single sideband which follows the modulating waveform
-
no sideband structure
Correct answer: a frequency which varies with the modulating waveform
In frequency modulation (FM), the information is carried by changes in the frequency of the carrier signal.
The instantaneous frequency of the transmitted signal varies in accordance with the modulating waveform, while the amplitude remains essentially constant.
- Amplitude variation describes AM.
- A single sideband is characteristic of SSB.
- FM produces sidebands, so it does not have a "no sideband" structure.
Therefore, the signal has a frequency which varies with the modulating waveform.
Last edited by jim.carroll. Register to edit
Tags: none
The signal from a balanced modulator consists of
-
a carrier and two sidebands
-
a carrier and one sideband
-
Correct Answerno carrier and two sidebands
-
no carrier and one sideband
Correct answer: no carrier and two sidebands
A balanced modulator is designed to suppress the carrier while still producing both modulation products. When an audio signal modulates an RF carrier in a balanced modulator, the carrier components cancel, leaving only the upper and lower sidebands.
The output is therefore a double sideband suppressed carrier (DSB-SC) signal.
- a carrier and two sidebands describes conventional AM, not a balanced modulator.
- a carrier and one sideband does not occur in normal modulation schemes.
- no carrier and one sideband describes a final SSB signal after filtering, not the direct output of the balanced modulator.
Therefore, the signal from a balanced modulator consists of no carrier and two sidebands.
Last edited by jim.carroll. Register to edit
Tags: none
The signal from a CW transmitter consists of
-
a continuous, unmodulated RF waveform
-
a continuous RF waveform modulated with an 800 Hz Morse signal
-
Correct Answeran RF waveform which is keyed on and off to form Morse characters
-
a continuous RF waveform which changes frequency in synchronism with an applied Morse signal
Tags: none
Correct answer: FM
A non-linear amplifier can be used when the amplitude of the signal is not required to remain constant.
FM (Frequency Modulation) carries information in the frequency variations of the carrier, not in its amplitude. Therefore, slight changes in amplitude caused by non-linear amplification do not affect the transmitted information.
- SSB, AM, and DSBSC carry information in amplitude variations.
- Non-linear amplification would distort these amplitude-modulated signals.
Therefore, FM can be amplified using a non-linear amplifier.
Last edited by jim.carroll. Register to edit
Tags: none
View Privacy Policy | Get help with HamStudy.org™
