The Radio Receiver
Receiver Block Diagrams
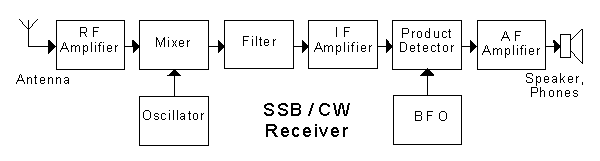
In the block diagram of the receiver shown, the "RF amplifier"
-
decreases random fluctuation noise
-
is a restoring filter amplifier
-
Correct Answerincreases the incoming signal level
-
changes the signal frequency
Tags: none

In the block diagram of the receiver shown, the "mixer"
-
Correct Answercombines signals at two different frequencies to produce one at an intermediate frequency
-
combines sidebands to produce a stronger signal
-
discriminates against SSB and AM signals
-
inserts a carrier wave to produce a true FM signal
Tags: none

In the block diagram of the receiver shown, the output frequency of the "oscillator" is
-
the same as that of the incoming received signal
-
the same as that of the IF frequency
-
Correct Answerdifferent from both the incoming signal and IF frequencies
-
at a low audio frequency
Tags: none

In the block diagram of the receiver shown, the "filter" rejects
-
AM and RTTY signals
-
Correct Answerunwanted mixer outputs
-
noise bursts
-
broadcast band signals
Tags: none

In the block diagram of the receiver shown, the "IF amplifier" is an
-
isolation frequency amplifier
-
intelligence frequency amplifier
-
indeterminate frequency amplifier
-
Correct Answerintermediate frequency amplifier
Tags: none

In the block diagram of the receiver shown, the "product detector"
-
produces an 800 Hz beat note
-
separates CW and SSB signals
-
rejects AM signals
-
Correct Answertranslates signals to audio frequencies
Tags: none

In the block diagram of the receiver shown, the "AF amplifier"
-
rejects AM and RTTY signals
-
Correct Answeramplifies audio frequency signals
-
has a very narrow passband
-
restores ambiance to the audio
Tags: none

In the block diagram of the receiver shown, the "BFO" stands for
-
bad frequency obscurer
-
basic frequency oscillator
-
Correct Answerbeat frequency oscillator
-
band filter oscillator
Tags: none

In the block diagram of the receiver shown, most of the receiver gain is in the
-
RF amplifier
-
Correct AnswerIF amplifier
-
AF amplifier
-
mixer
Correct answer: IF amplifier
In a superheterodyne receiver, most of the receiver’s gain is provided in the intermediate frequency (IF) amplifier stage. Operating at a fixed frequency allows high gain, stable amplification, and precise filtering without instability or tuning issues.
The RF amplifier provides only moderate gain, mainly to improve sensitivity and reduce noise and image responses. The audio amplifier increases signal level for the speaker or headphones, but it does not contribute to RF sensitivity. The mixer performs frequency conversion and typically has little or no gain.
- RF amplifier provides limited gain and is primarily used for noise performance and front-end selectivity.
- AF amplifier increases audio power for listening but does not improve RF signal sensitivity.
- mixer mainly performs frequency conversion and does not provide significant gain.
Therefore, most of the receiver gain is in the IF amplifier.
Last edited by jim.carroll. Register to edit
Tags: none
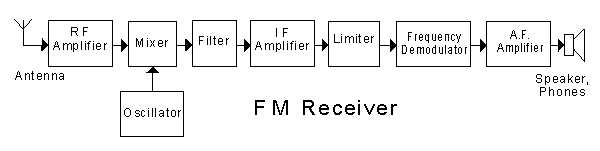
In the block diagram of the receiver shown, the "RF amplifier"
-
decreases random fluctuation noise
-
masks strong noise
-
Correct Answershould produce little internal noise
-
changes the signal frequency
Correct answer: should produce little internal noise
The RF amplifier is the first active stage in the receiver and amplifies very weak incoming signals from the antenna.
To preserve signal quality, it must:
- introduce as little internal noise as possible
- maintain a good signal-to-noise ratio
Any noise added at this stage will be amplified by all following stages.
- It does not decrease random noise.
- It does not mask strong noise.
- Frequency conversion occurs in the mixer stage.
Therefore, the RF amplifier should produce little internal noise.
Last edited by jim.carroll. Register to edit
Tags: none

In the block diagram of the receiver shown, the "mixer"
-
Correct Answerchanges the signal frequency
-
rejects SSB and CW signals
-
protects against receiver overload
-
limits the noise on the signal
Tags: none

In the receiver shown, when receiving a signal, the output frequency of the "oscillator" is
-
the same as that of the signal
-
the same as that of the IF amplifier
-
Correct Answerof constant amplitude and frequency
-
passed through the following filter
Correct answer: of constant amplitude and frequency
In a superheterodyne receiver, the local oscillator generates a stable signal which is mixed with the incoming RF signal.
The purpose of this mixing process is to produce an intermediate frequency (IF):
\[ f_{\text{IF}} = |f_{\text{RF}} - f_{\text{LO}}| \]
To ensure proper operation and stable IF output, the oscillator must provide a signal of:
-
constant amplitude
-
constant frequency (for a given tuning setting)
-
It is not the same frequency as the received signal.
-
The IF is produced after mixing.
-
The oscillator output itself is not passed through the following RF filter.
Therefore, the oscillator output is of constant amplitude and frequency.
Last edited by jim.carroll. Register to edit
Tags: none

In the block diagram of the receiver shown, the "limiter"
-
Correct Answerlimits the signal to a constant amplitude
-
rejects SSB and CW signals
-
limits the frequency shift of the signal
-
limits the phase shift of the signal
The demodulator will usually be a "discriminator" and may even be of a "phase-lock-loop" variety. There will be a "limiter" before the descriminator to remove noise peaks and amplitude-changes before detection of the FM signal
Last edited by cmscouler. Register to edit
Tags: none

In the block diagram of the receiver shown, the "frequency demodulator" could be implemented with a
-
product detector
-
Correct Answerphase-locked loop
-
full-wave rectifier
-
low-pass filter
The demodulator will usually be a "discriminator" and may even be of a "phase-lock-loop" variety.
Last edited by cmscouler. Register to edit
Tags: none

In the block diagram of the receiver shown, the "AF amplifier"
-
amplifies stereo signals
-
Correct Answeramplifies speech frequencies
-
is an all frequency amplifier
-
must be fitted with a tone control
Tags: none

In this receiver, an audio frequency gain control would be associated with the block labelled
-
Correct AnswerAF amplifier
-
frequency demodulator
-
speaker, phones
-
IF amplifier
Tags: none

In the block diagram of the receiver shown, the selectivity would be set by the
-
AF amplifier
-
mixer
-
limiter
-
Correct Answerfilter
Correct answer: filter
Selectivity in a receiver is its ability to accept the desired signal while rejecting signals on nearby frequencies.
In a superheterodyne FM receiver, this is mainly determined by the IF filter, which defines the receiver’s bandwidth.
The filter allows the desired IF signal to pass while attenuating adjacent unwanted signals.
- The AF amplifier operates after demodulation and does not affect RF selectivity.
- The mixer converts frequencies but does not determine bandwidth.
- The limiter removes amplitude variations, not unwanted frequencies.
Therefore, receiver selectivity is set by the filter.
Last edited by jim.carroll. Register to edit
Tags: none

In the FM communications receiver shown in the block diagram, the "filter" bandwidth is typically
-
3 kHz
-
Correct Answer10 kHz
-
64 kHz
-
128 kHz
Correct answer: 10 kHz
In an FM receiver, the filter following the mixer is the IF filter, which determines the receiver’s bandwidth.
For typical narrowband FM voice communication, the transmitted signal bandwidth is determined by:
\[ B \approx 2(\Delta f + f_m) \]
where:
- \(\Delta f\) is the frequency deviation (typically about \(2.5\ \mathrm{kHz}\))
- \(f_m\) is the highest modulating frequency (typically about \(3\ \mathrm{kHz}\))
Substituting:
\[ B \approx 2(2.5 + 3) = 11\ \mathrm{kHz} \]
So an IF filter bandwidth of about 10 kHz is suitable for passing the FM signal without excessive distortion.
- 3 kHz is appropriate for AM or SSB audio bandwidth, not FM IF bandwidth.
- 64 kHz and 128 kHz are far wider than required for narrowband FM and would admit excessive noise.
Therefore, the filter bandwidth is typically 10 kHz.
Last edited by jim.carroll. Register to edit
Tags: none

In the block diagram of the receiver shown, an automatic gain control (AGC) circuit would be associated with the
-
Speaker
-
Correct AnswerIF amplifier
-
RF filter
-
Oscillator
Tags: none

In the block diagram of the receiver shown, the waveform produced by the "oscillator" would ideally be a
-
square wave
-
pulsed wave
-
Correct Answersinewave
-
hybrid frequency wave
Tags: none
View Privacy Policy | Get help with HamStudy.org™
